An alternative to traditional brainstorming that fuses visualization and group brainstorming techniques to drive innovative action
Brainstorming emerged as a transformative tool in the early 20th century when Alex Osborn, a luminary in advertising, unveiled this innovative approach to problem-solving in his 1953 opus, "Applied Imagination." His work established the foundational principles of brainstorming, which emphasizes the freedom of thought and the power of collective ideation. He was convinced that prevailing problem-solving tactics suffered from an over-reliance on conventional methods, stifling creativity in the process. Osborn championed group brainstorming sessions as fertile grounds for producing a plethora of ideas, regardless of their eccentricity or initial impracticality.
In the subsequent decades, brainstorming has become a staple in professional circles. Its influence has reached diverse fields, such as consumer research, marketing, service improvement, and new product development. Brainstorming has undoubtedly established itself as an indispensable ally of innovation and creativity.
However, traditional brainstorming has its challenges. It has been observed that within brainstorming sessions, some individuals with more assertive personalities may overpower the conversation, thereby reducing the variety of viewpoints and stifling potential creativity - a phenomenon recognized as social loafing. When group work doesn't foster individual efforts, the outcome is often a skewed and limited range of ideas, which can be further restricted by dominant individuals.
A related issue is production blocking, wherein others unintentionally suppress the contributions of some group members. As the size of the group swells, sumind mapping softwarech disruptions also increase. Further complicating matters is evaluation apprehension, which can lead to participants withholding innovative ideas due to fear of criticism, subsequently hampering efficiency.
The brainstorming process can further become constrained by topic fixation, where the group becomes overly focused on a single idea to the detriment of exploring alternative concepts. The absence of anonymity in traditional brainstorming can also inhibit participants from offering unorthodox ideas due to concerns about potential backlash. Groupthink, a situation where the group collectively leans towards a certain consensus without scrutinizing alternatives, often surfaces during brainstorming, exacerbating these challenges. The participation of numerous or inappropriate members in a session further contributes to a disordered atmosphere, undermining the orderly exchange of ideas.
A lack of structure and skilled facilitation will also hinder the brainstorming process, with participants jumping from one idea to the next without any clear direction or focus. This lack of structure often leads to a large number of ideas being generated, but many of these ideas are unfocused or unrealistic. Finally, brainstorming often lacks follow-through, with many of the ideas generated during a session failing to materialize into concrete actions or innovations.
This e-book presents a powerful evolution of traditional brainstorming, called mindstorming, designed to address these shortcomings.
At the heart of innovation lies the mindstorm - a potent fusion of visualization techniques and group brainstorming that elevates idea generation and decision-making to new heights. It calls upon visual tools like mind mapping, transforming thoughts, concepts, and data into a hierarchical visual landscape. This perspective allows teams to perceive connections, patterns, and relationships that might have remained obscure otherwise. By harnessing the power of visualizations, teams navigate complex problems and spark fresh insights, perspectives, and ideas.
Mindstorming provides a visual and structured framework for the brainstorming process, preventing the chaos often associated with traditional brainstorming sessions. By incorporating a clear direction and focus, participants generate more focused and realistic ideas, ultimately resulting in higher-quality outcomes.
Employing visualization techniques in conjunction with a disciplined brainstorming approach, mindstorming resolves issues inherent to traditional brainstorming. For instance, the visual tools used in mindstorming counteract the dominance of assertive personalities, ensuring a balanced and inclusive conversation. Through mind maps, participants can visually organize their thoughts, leading to a variety of perspectives that create a fertile environment for creativity.
Affinity diagrams, another visualization tool employed in mindstorming, counteract production blocking by enabling participants to group similar ideas. This collective process ensures that all voices are represented, and prevents individuals from unintentionally obstructing others during discussions. Affinity diagrams also address the challenge of topic fixation, broadening the scope of idea exploration.
Mindstorming mitigates evaluation apprehension and fosters an open atmosphere by implementing matrices for idea prioritization. As ideas are classified based on shared criteria, participants can confidently put forward nonconventional ideas without apprehension of undue criticism. This also assists in countering groupthink by promoting critical analysis of ideas and encouraging a culture of constructive feedback.
The visual foundation of mindstorming enhances accountability and follow-through, with ideas systematically documented and readily available for future reference. This transparency encourages participants to take responsibility for their contributions, and ensures that the ideas generated evolve into concrete actions or innovations.
In essence, mindstorming presents a superior approach to brainstorming, empowering teams to foster creative ideas, tackle groupthink, and propel the most promising ideas to fruition.
Visualization is a frequently underused resource in ideation, which has immense potential for transforming business outcomes.
Informally, many managers and teams are already capitalizing on this tool, brainstorming on unconventional platforms like whiteboards, butcher papers, or even napkins. Such simple visualization exercises facilitate uncovering innovative perspectives and solutions to complex problems such as restructuring an organization, creating novel business processes, or systematizing decision-making.
Visualizations bring a plethora of advantages to the table—planning, execution, and follow-up of brainstorming sessions all stand to benefit. Studies have unequivocally shown the efficacy of visualizations in sparking creativity and generating pioneering ideas. Coupling brainstorming with visualization gives rise to "mindstorming", an effective process for problem-solving and innovation across various fields.
Many studies affirm that these visualizations can enhance memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills. One study, in particular, revealed the positive impact of visual imagery training on mental rotation tasks. Participants with this training exhibited significant improvements in both the speed and accuracy of these tasks.
Using mind maps can enhance the articulation of ideas. Research conducted by the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and Virginia Tech demonstrated that students who employed mind maps for brainstorming were more successful in conveying their ideas to others compared to those who refrained from using mind maps.
Another university study highlighted how the mind mapping process encourages creative thinking, enhancing and speeding up the ability to generate, visualize and organize ideas. Participants noted the potential of this technique to present alternative approaches to a topic, leading them to discover novel insights and information sources.
Visualization techniques like mind mapping can enhance metacognitive skills, one's ability to understand, control, and evaluate their own learning and thinking processes, enabling individuals and teams to visually track the progression of their ideas, see how different concepts connect, and adjust their thinking strategies as necessary.
In a 2021 survey in the Mind Mapping Software Blog, mind mappers reported the top benefit of mind mapping as an improved understanding of complex issues while increased knowledge capture/organization, reaching clarity of thinking faster, increasing organization, and enhancing their ability to synthesize information round out the top five benefits of visualizing information.
Mind mapping helps them distill information and reach clarity faster
Mind mapping helps them share their ideas with greater clarity and impact
Mind mapping helps them manage projects more efficiently
Mind mapping helps them identify the root causes of business problems
Visualization is a potent cognitive tool that bolsters memory, concentration, problem-solving skills, creativity, idea generation, and innovation. The scientific consensus supports employing visual strategies across diverse fields, including cognitive neuroscience and business management.
In light of these benefits, individuals and organizations should consider integrating visualization strategies into their workflows to optimize success.
Planning a brainstorming session with visualizations, for instance, has numerous advantages. A primary benefit is the ability to envision the broader objective, fostering alignment among team members around a shared vision and common goals. Additionally, visualizations can reveal potential obstacles or areas requiring further research, empowering teams to address these proactively.
Visualizations are invaluable tools for organizing and categorizing ideas during a brainstorming session. Visual idea mapping can unveil patterns and connections otherwise hidden, leading to discovering new ideas and insights that traditional brainstorming methods may overlook. This can lead to the discovery of new ideas and insights that would not have been possible with traditional brainstorming methods.
Visualizations also help keep teams on track and focused, ensuring that they generate ideas that are directly related to the task at hand. Visualizing information through tools like mind maps can enhance critical thinking, which in turn can lead to innovative solutions to challenging problems.
Finally, visualizations are transformative during a brainstorming session when it comes to organizing, prioritizing, and selecting ideas to turn into projects. Visual aids allow teams to easily identify promising ideas and plan their execution. Documenting ideas visually simplifies revisiting and further developing them if required, thus enhancing communication and ensuring consensus. Visualizations fortify support for new projects and initiatives.
The benefits of visualizations for planning, executing, and following up on brainstorming sessions are evident. They facilitate team alignment around shared goals, generate new ideas and insights, maintain focus, and prevent idea loss. Therefore, the use of visualizations alongside brainstorming should be a fundamental strategy for any team aiming to augment their creativity and innovation.
Mindstorming requires a significant shift in process from traditional brainstorming. Here are the steps to mastering the mindstorming process.
Planning and laying a strong foundation are invaluable steps toward ensuring a productive and successful mindstorm session. Preparation sets the stage, creating a clear path to follow during the session, which allows participants to focus their energies on creative and critical thinking. It ensures that the participants, the problem at hand, and the mindstorming process are fully understood and aligned, fostering a smooth, efficient, and effective mindstorming session.
Indeed, when it comes to planning, employing a mind map as a strategic tool can enhance the process significantly. A mind map serves as a visual guide, allowing you to structure, manage, and navigate the various stages of planning more efficiently. It helps you break down the preparation process into manageable steps, from defining the objective to laying out the ground rules. The graphical nature of a mind map makes it easier to see connections and relationships between different parts of the planning process, promoting a more holistic understanding.
Mind maps foster a more dynamic and flexible approach, enabling you to easily adapt your plan as the need arises. Using a mind map to guide your planning process not only offers a clear and organized pathway towards a successful mindstorming session but also encourages a more comprehensive and innovative approach to problem-solving. It is your visual roadmap to success, charting a clear course through the various stages of preparation while fostering creativity, clarity, and collaboration.
The launching pad for a productive mindstorming session is a clear understanding of the problem or goal at hand. It could be a challenging issue or a promising opportunity the organization encounters. The importance of this step is monumental, as it paves the way for the subsequent stages of the session.
Following the clear articulation of the problem or goal, the assembly of the participating individuals forms the next phase. A successful mindstorming session hinges on the diversity of perspectives and proficiencies within the group. Individuals who are receptive to fresh ideas and have a collaborative mindset form the ideal participants for such a session.
Choosing a competent facilitator is an integral element of a rewarding mindstorming session. This individual should possess a comprehensive understanding of the identified problem or goal and have the ability to guide the discourse, keeping it focused and on track. The facilitator also creates an environment where all participants feel empowered to voice their ideas.
Subsequently, the format and location of the mindstorming session need to be determined. Considerations include whether the session will be conducted in-person or virtually, whether it's a standalone meeting or a series, and whether it will encompass group activities or individual ideation. The choices made in this step directly impact the overall productivity of the session.
The preparation of materials and tools is a crucial step in ensuring an efficient and effective mindstorming session. This could encompass items such as notepads, markers, whiteboards, and other visualization tools. Preparing in advance may also involve formulating thought-provoking prompts or questions to steer the conversation constructively.
Before the ignition of the mindstorming session, laying out ground rules for the discussion is paramount. This might include fostering respectful communication, creating guidelines for brainstorming and idea sharing, and setting clear expectations for active participation. By establishing these rules upfront, the session can proceed in a productive and respectful manner to all participants.
As we delve into the rich potential of mindstorming, Steve Jobs' insight is a guiding light. The power of teamwork and collective intelligence is central to this process. Through pooling our unique perspectives, talents, and experiences, we open the doors to a more creative and holistic problem-solving approach.
This collective endeavor not only enriches our outcomes but also fosters a vibrant culture of mutual respect, dynamic collaboration, and shared growth. The following steps are designed to create this synergistic environment, where creativity and innovation are nurtured, and every voice is valued and heard.
Prior to diving into the session, establish a set of ground rules for the upcoming discussion. These could cover aspects of respectful communication, protocols for brainstorming and sharing ideas, and expectations for active participation. Setting these parameters early on sets the stage for a constructive and fruitful dialogue.
Commence the session with an exercise designed to spark creativity and stimulate the brain. Studies reveal that engaging in activities unrelated to the primary task can spur creative thinking. Be it improvisation games, lateral thinking puzzles, or quick brainstorming tasks on unrelated topics, these exercises serve to relax participants, boost cognitive flexibility, and prime their minds for creative ideation.
Once the minds are warmed up, revisit the problem or goal that was defined during the preparatory stage, and provide any additional context or background information. Sharing information from diverse sources or perspectives enables participants to approach the problem from various angles, encouraging divergent thinking and innovative solutions. Encourage participants to think expansively, entertain unconventional ideas, and challenge the status quo.
Present the visual tools selected for the session and offer guidance. Consider introducing digital platforms or applications that facilitate real-time collaboration and offer diverse visualization options, such as mind mapping software or virtual whiteboards. These tools can capture ideas more effectively and enable participants to interact with the visualizations, contributing to their creation and organization.
Harness a variety of visual techniques to stimulate divergent thinking. Below are some example visualizations utilized for various ideation sessions focused on solving business problems, expanding product lines, and more.
A mind map is a visual tool that helps to organize thoughts and ideas around a central theme or problem. Starting from a central idea, branches of related ideas or sub-themes are drawn, helping to visualize connections and hierarchies between concepts. In mindstorming, mind maps can facilitate idea generation, aid in the visualization of thoughts, and help structure these thoughts meaningfully. It's akin to conversing with your brain, visually tracking the flow of ideas and their interconnectedness.
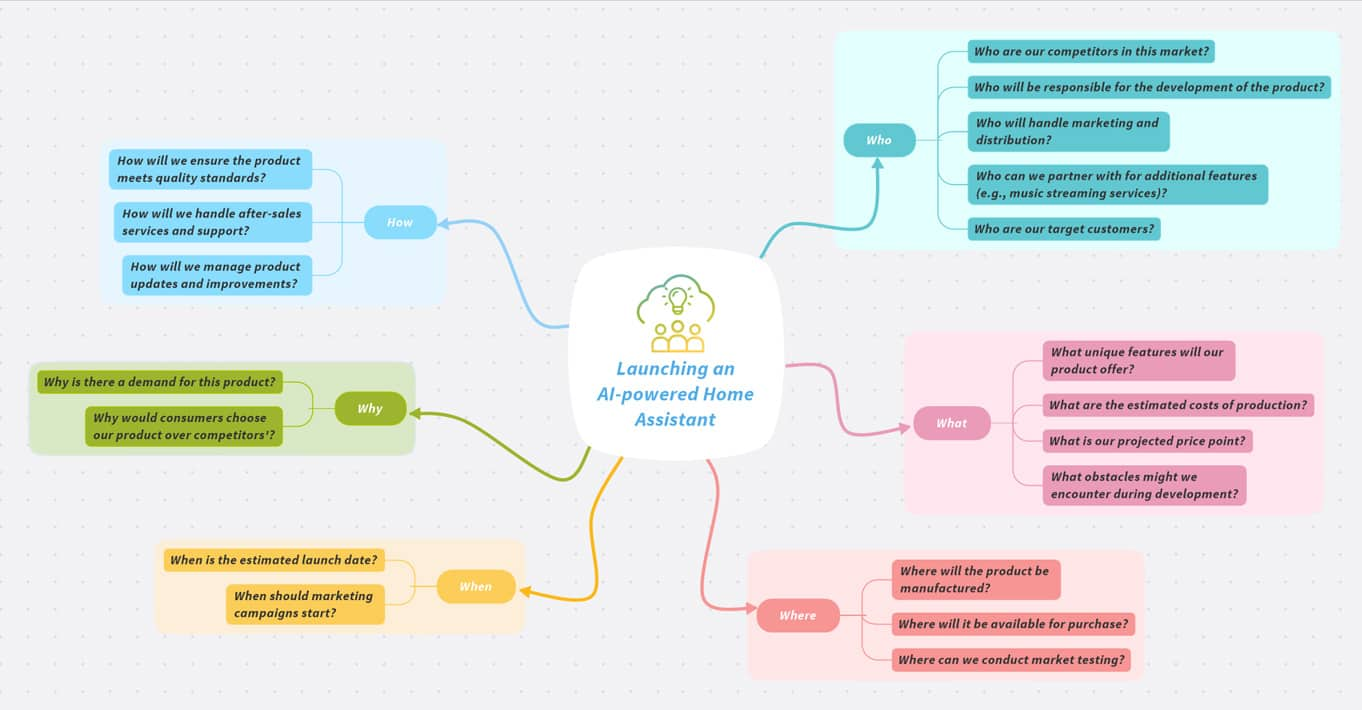
This technique uses a six-pointed star to question a central idea or problem. Each point of the star represents a different question category (Who, What, Where, When, Why, How). Star bursting helps to expand thinking by encouraging the exploration of diverse scenarios and possibilities related to the central problem. It allows for a comprehensive understanding of the problem or opportunity, which can lead to innovative solutions during a mindstorming session.
This is an acronym for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Rearrange. It's a method for thinking about problems or ideas in new ways. Each word in the acronym prompts a question that encourages you to think differently about the idea or problem at hand. SCAMPER aids in generating innovative solutions and helps to rethink stale ideas, making it an integral part of the mindstorming process.
This visual tool represents ideas, concepts, and the relationships between them. Concept maps can include arrows or lines that connect related ideas, showing how one concept relates to another. In mindstorming, concept maps are useful for structuring and organizing thoughts, ideas, and knowledge. They help teams visualize connections between different elements of a problem or idea, promoting a more holistic understanding.
This stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It's a framework used to assess the internal and external factors that could affect the success of a project, product, or business. In mindstorming, a SWOT analysis can help teams identify potential challenges and opportunities, fostering proactive thinking and strategic planning.
These are graphical representations of a process or system, showing the sequence of steps involved. Each step is represented by a different symbol and is connected to the next step by a line or arrow. Flowcharts are invaluable in mindstorming as they help teams visualize processes, identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and generate solutions for improvement. They provide a clear, step-by-step visual of a process, aiding in understanding and problem-solving.
Cultivate an atmosphere of openness and support by underscoring the significance of psychological safety. Studies show that individuals are more likely to share unorthodox ideas and take risks when they feel safe and supported. Validate all contributions, discourage criticism or judgment, and promote active listening and empathy. This welcoming environment will encourage participants to share their ideas more freely, leading to a broader and more diverse array of perspectives and solutions.
The power of a mindstorming session lies not just in the plethora of ideas it generates but in the concrete actions that ensue. Picasso's words are a reminder that taking the leap from ideation to action is a vital step in the journey to success. Through the concerted efforts of a team, ideas born in the vortex of a mindstorming session transform into viable solutions, capable of sparking innovation and catalyzing change.
The following steps will outline the process of turning these ideas into action - from clarifying and organizing ideas to refining them and finally to the execution phase, where we witness the fruits of our collective creative endeavor.
Planning and completing a mindstorming session are the first parts of the journey. The challenge that follows is transforming the flood of ideas into concrete actions. This involves organizing, prioritizing, and implementing the best ideas that have emerged from the session. Visualization tools can add value to this process, providing a visual structure to the assortment of ideas.
For instance, the mindstorm may have had the objective of “Declining customer satisfaction levels due to delays in customer service response time.”
And the mindstorming session would typically yield a list of potential solutions.
The following steps discuss how to clarify, organize, prioritize and ultimately plan the process needed to turn ideas into powerful actions that resolve issues and deliver innovations to the market.
After a mindstorming session, the first step is to ensure all ideas are properly understood. Ask participants to elaborate on their suggestions, providing context and clarification. This step is crucial as it ensures every idea is fully comprehended, which is critical for effective evaluation. Mind maps can be used to prompt further discussion and evaluation of each idea.
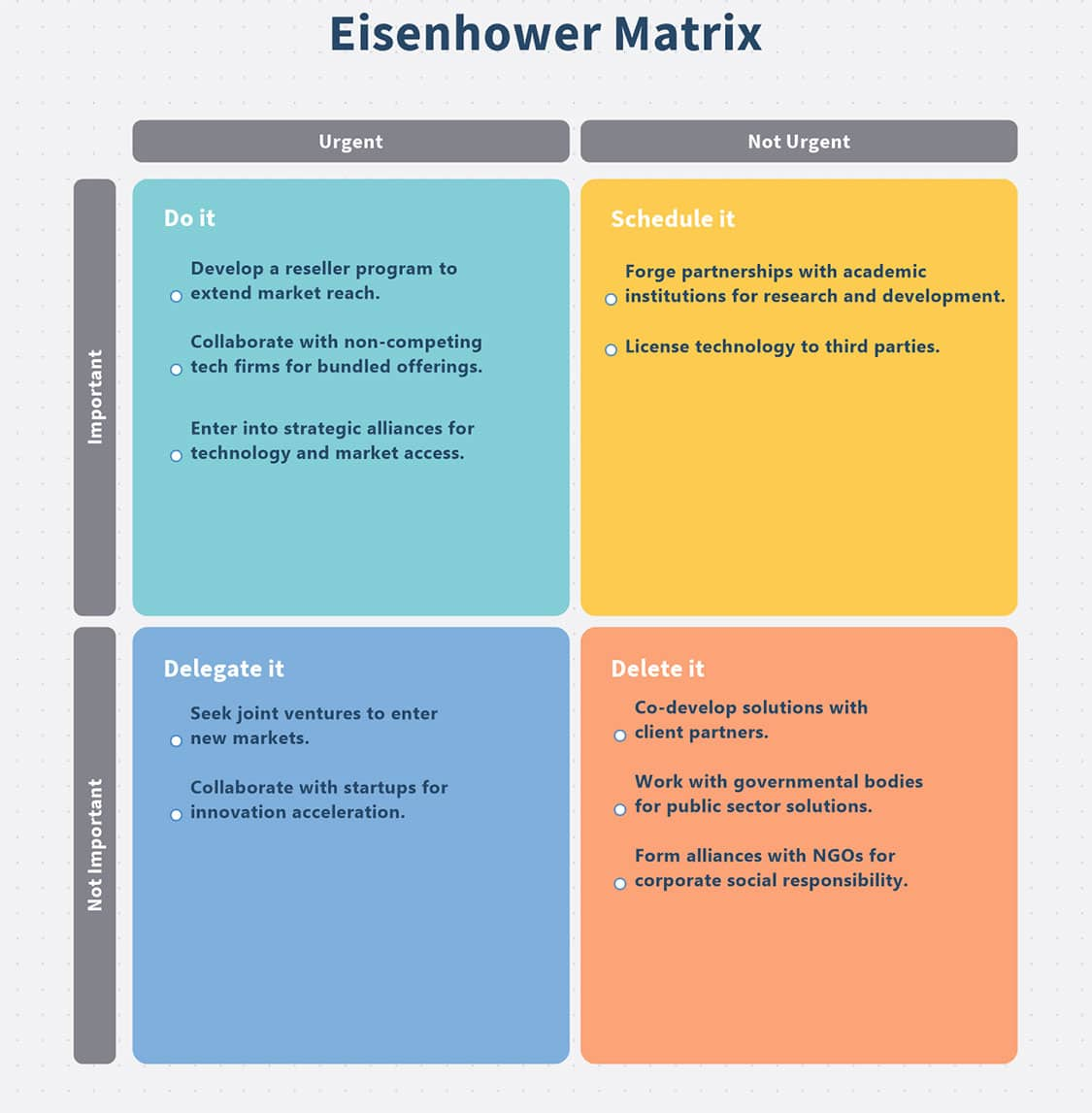
Once the ideas are clarified, it's time to evaluate them. This process could involve a decision matrix or voting system. Encourage participants to consider practical factors like feasibility, potential impact, and how well the idea aligns with the defined objective. Based on these criteria, the ideas can be prioritized.
To better organize the ideas, affinity diagrams can be used. This technique involves categorizing ideas based on their similarity or relationship. Creating a visual representation of the ideas can aid in spotting patterns and themes.
Once organized, prioritizing the ideas comes next. Tools such as the impact-effort matrix can help with this. Each idea is assessed based on its potential impact and the effort required to implement it. High-impact, low-effort ideas are prioritized, while low-impact, high-effort ideas might be set aside.
A decision matrix can also aid in this process. Each idea is evaluated against criteria like feasibility, impact, and alignment with company goals. Each criterion is weighed according to its importance, and each idea is scored against these criteria. The weighted scores can then be used to prioritize the ideas.
In the example below, an idea is evaluated with the RICE scoring method. The RICE method is a model used to help businesses make decisions by evaluating and prioritizing ideas based on a weighted score. The acronym stands for Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort.
The RICE score is then calculated as:
Ideas or tasks with the highest RICE scores should be the highest priority, as they offer the most "bang for the buck" – the greatest effect for the least effort, adjusted for the reach of the idea and your confidence in your estimates.
This method aids in the decision-making process by helping teams reach a consensus and make data-driven decisions rather than based purely on gut feelings or opinions.
Now that the top ideas have been identified, the next step is to develop an actionable plan for their implementation. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and establish a process to track progress.
A visual roadmap and Gantt charts can then be created to communicate these prioritized ideas and the steps required for implementation. This roadmap can ensure that the team remains focused on key tasks and that progress is made toward achieving the desired outcomes.
Mind mapping can also be a powerful tool in this process. The decision can be placed at the center of the mind map, and branches can represent major components of the project, such as milestones or deliverables. These branches can further be divided into sub-branches, representing individual tasks. This ensures each task is actionable and has a clear owner.
By indicating dependencies between tasks and using color -coding or symbols to show the priority or status of tasks, mind maps can provide a clear visual guide to the project plan. This can enhance creativity, improved organization, increased productivity, better collaboration, and more informed decision-making. Ultimately, mind maps can streamline the project management process, enhancing communication and leading to more effective outcomes.
After the conclusion of the session, conduct a review of key takeaways and a discussion of valuable insights gleaned. Acknowledge everyone's contributions and encourage participants to keep reflecting on the ideas generated and how they can be applied in their work.
After the session, it's crucial to share the outcomes with all participants, including the visualizations and documented ideas. This step maintains momentum, fosters accountability, and ensures that the action plan is executed.
Mind mapping offers a robust means of transmuting the aftermath of a brainstorming session, the decision, into a well-articulated project plan. Start by inscribing the decision at the heart of the mind map, establishing it as the central idea. Following this, introduce branches that signify the principal components of the project, such as key milestones or deliverables.
These primary branches can further be segmented into sub-branches, each representing individual tasks needed to accomplish a particular component. To ensure a comprehensive project plan, refine these sub-branches into detailed sub-tasks. Remember, each sub-task must be actionable and assigned to a clear owner for effective execution.
Mind mapping serves the additional purpose of identifying interdependencies between tasks. By drawing connecting lines between tasks, it becomes evident which tasks rely on others and which can proceed independently.
For a clear status overview, incorporate color -coding and symbols. This could mean using green to indicate tasks on schedule, yellow for tasks requiring attention, and red for tasks potentially causing delays.
The mind map becomes a communicative tool with the project plan fully delineated. Share the plan with stakeholders and team members by exporting the mind map to a project management tool or distributing printed copies during a meeting.
Employing mind mapping to chart a project plan ensures the project is distilled into actionable tasks with defined owners and dependencies. This approach not only increases the likelihood of success and reduces the risk of delays or missed deadlines, but it also offers multiple benefits:
Overall, mind maps streamline the project management process, enhance collaboration and communication, and pave the way for effective and efficient project outcomes.
With the spirit of innovation at its heart, mindstorming breathes life into Alan Kay's assertion that shaping the future is within our power. This chapter delves into how this dynamic methodology empowers creatives, executives, marketers, and professionals across the board to become architects of the future. Through mindstorming, each role finds a unique conduit for innovation, collaboration, and strategic thinking, fostering not just personal growth but propelling entire organizations to new heights.
This chapter unravels the magic of mindstorming as it breathes life into ideas, empowering creatives to manifest new realities, executives to steer vision, and marketers to captivate the marketplace. From product managers building impactful solutions to project managers navigating complex terrains, mindstorming serves as a dynamic tool, sparking innovation at every turn.
Our journey reveals how mindstorming equips you with the power to invent your future, lighting the path to groundbreaking insights. Together, we'll witness how it propels organizations to unprecedented heights, embodying Alan Kay's vision, where we predict the future by inventing it.
Mindstorming for creatives: unleashing potential |
Mindstorming for executives: steering the vision |
Mindstorming for marketing: engaging the market |
|
| Uses | Generates fresh perspectives, stimulates innovative thinking, and creates a mental space for creative exploration without judgment. | Creates a detailed mental picture of potential business opportunities, risks, and solutions. | Enhances understanding of target audiences and unlocks a broader scope for creative ideation. |
| Benefits |
|
|
|
Mindstorming for product managers: building relevant solutions |
Mindstorming for project managers & project teams: navigating project complexity |
Mindstorming for R&D: cultivating innovation |
Mindstorming for sales: amplifying engagement and boosting sales momentum |
|
| Uses | Fuels collective creativity and assists in spotting opportunities and gaps within the product portfolio | Serves as a platform for developing inventive solutions and proactively identifying project risks. | Unleashes new insights and ideas, assists in swift decision-making, and aids in identifying project risks. | Serves as a tool for deep insights, aids in speedy decision-making, and facilitates the optimization of sales strategies. |
| Benefits |
|
|
|
|
The versatility of mindstorming sets it apart, proving its relevance and applicability across diverse functions, be it product management, project teams, R&D, IT, sales, or business development. This universal appeal is driven by its unique capacity to ignite creativity and drive innovation, no matter the complexity or nature of the problem at hand. The visualization methodologies employed in mindstorming bring to light hidden insights and ideas that traditional brainstorming could potentially overlook, leading to a broader spectrum of solutions and deeper comprehension of the problem or opportunity.
Mindstorming enhances and accelerates decision-making. The visual representation of data and information allows teams to promptly highlight and prioritize essential aspects, resulting in a more precise and rapid decision-making process. Additionally, this visual aid serves as an early detection system for possible risks and impediments, empowering teams to proactively counter these challenges before they spiral out of control - a functionality traditional brainstorming often lacks.
On the soft skills front, mindstorming bolsters collaboration and communication. It nurtures a culture of transparency and mutual respect, forging a positive and high-performing work environment. The spirit of inclusivity and collaboration embedded in mindstorming promotes diverse thought and broadens perspectives - pivotal elements for fostering innovation and growth.
In terms of process optimization, mindstorming excels with its visual capabilities. By mapping out entire project plans, sales processes, or product development cycles, teams can spot bottlenecks and optimize efficiencies, thereby driving improved outcomes and performance. This visual advantage is often absent in traditional brainstorming, making it less effective in pinpointing process inefficiencies.
Perhaps the most compelling facet of mindstorming is its ability to nurture an environment of innovation and adaptability. It instills a dynamic and creative approach to problem-solving within teams, transforming the organization into a hub of agility and flexibility. In our rapidly shifting world, this ability to swiftly adjust to market and technological changes is more crucial than ever. Mindstorming empowers teams to think critically and creatively, tackling increasingly complex problems and identifying opportunities within the pace of change. This fosters resilience and responsiveness, equipping the organization to thrive amidst constant evolution.
To sum up, mindstorming—pairing visualization with brainstorming—is a powerful technique with far-reaching benefits across sectors and teams. Its prowess in sparking new ideas and insights, fine-tuning decision-making, bolstering collaboration and communication, optimizing processes, and nurturing an innovative culture position it as a superior methodology to traditional brainstorming. Thus, adopting mindstorming techniques emerges as a strategic move for any team aiming to realize their maximum potential for success in today's fast-paced and fiercely competitive business world.